Autoimmune Disorders: What Early Symptoms Might Indicate
Autoimmune disorders occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, leading to various health complications. Understanding the early warning signs is crucial for timely intervention and proper management. These conditions can affect any part of the body, from joints and muscles to organs and skin, making early recognition of symptoms particularly important for better health outcomes.
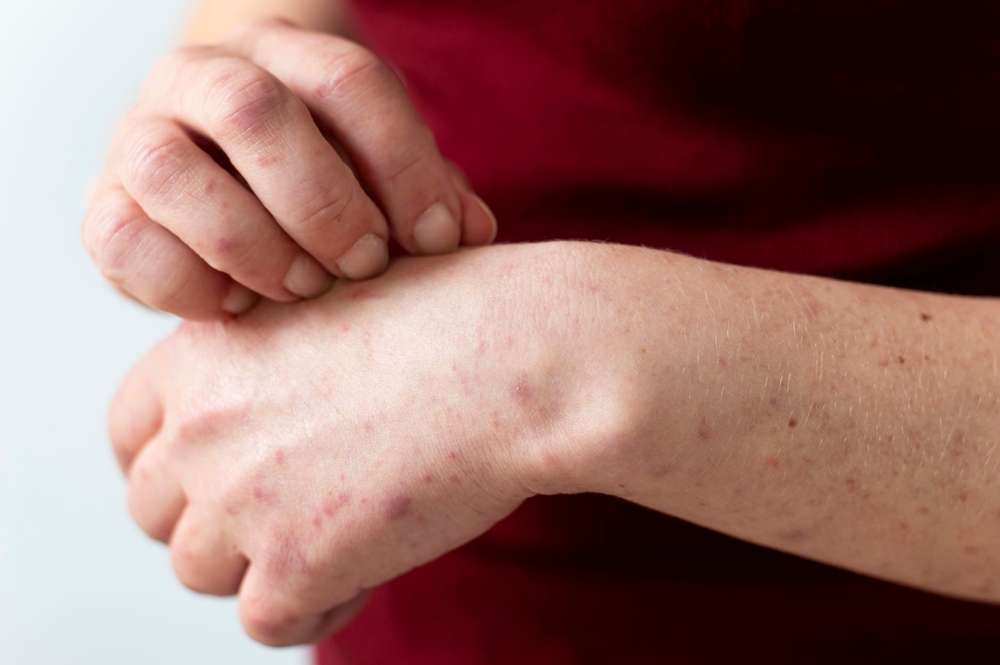
Understanding Common Autoimmune Disease Symptoms
The initial signs of autoimmune disorders often appear subtle and may resemble other common conditions. Fatigue is one of the most prevalent early symptoms, along with mild fever, general malaise, and joint pain. Many people experience these symptoms for months before receiving a proper diagnosis. Muscle weakness, recurring rashes, and unexplained weight changes can also signal the onset of an autoimmune condition.
Key Early Warning Signs to Monitor
Several distinctive signs may indicate the development of an autoimmune disorder:
-
Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
-
Joint pain and stiffness, especially in the morning
-
Skin problems, including rashes or color changes
-
Digestive issues and abdominal pain
-
Swollen glands in multiple areas
-
Recurring low-grade fever
-
Hair loss or skin changes
-
Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Obtaining an early diagnosis can significantly impact the management and progression of autoimmune disorders. When symptoms first appear, doctors typically conduct a series of tests, including:
-
Antinuclear antibody tests (ANA)
-
Complete blood count (CBC)
-
Comprehensive metabolic panel
-
Inflammation markers
-
Specific antibody tests related to suspected conditions
Common Types of Autoimmune Disorders
Different autoimmune conditions present varying combinations of symptoms:
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Primarily affects joints
-
Lupus: Can affect multiple organs and systems
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Impacts the central nervous system
-
Type 1 Diabetes: Affects insulin production
-
Psoriasis: Manifests as skin problems
-
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: Affects thyroid function
Risk Factors and Prevention
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing autoimmune disorders:
-
Family history of autoimmune conditions
-
Gender (women are more commonly affected)
-
Environmental triggers
-
Certain infections or viruses
-
Lifestyle factors such as stress and diet
Treatment Approaches and Management
Treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and severity:
-
Immunosuppressive medications
-
Anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Targeted biological therapies
-
Hormone replacement
-
Lifestyle modifications
-
Diet changes
-
Regular exercise
-
Stress management techniques
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




